Pre-intermediate level (A2)
some- in affirmative sentences We normally use something, somebody/someone, somewhere in affirmative sentences. Look! There’s something under that chair.
What’s the difference? Present Perfect and Past Simple Present Perfect Simple Past Simple Unfinished actions that started in the past and continue
The Present Perfect Tense is formed using the following structure: Affirmative: Subject + Have / Has + Past Participle Negative: Subject + Haven’
What are relative clauses? A relative clause is a subordinate clause that modifies a noun or a noun phrase. Example: The
Present continuous (future arrangements) We often use the present continuous to talk about the future, especially about future
Quick Summary Chart When to use GOING TO The structure BE GOING TO is normally used to indicate the future but with some type of connection to the present.
Contrast however However means ‘but’. However is normally used at the beginning of a sentence, before a comma
Purpose with to, in order to and so as to Use to , so as to, and in order to to express purpose in the affirmative form.
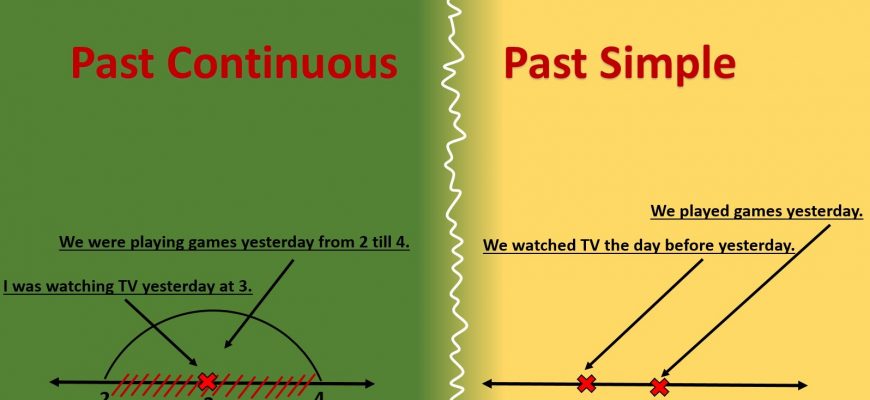
Grammar explanation The past continuous and the past simple help us to show how two past actions or situations are connected. Past simple The past simple
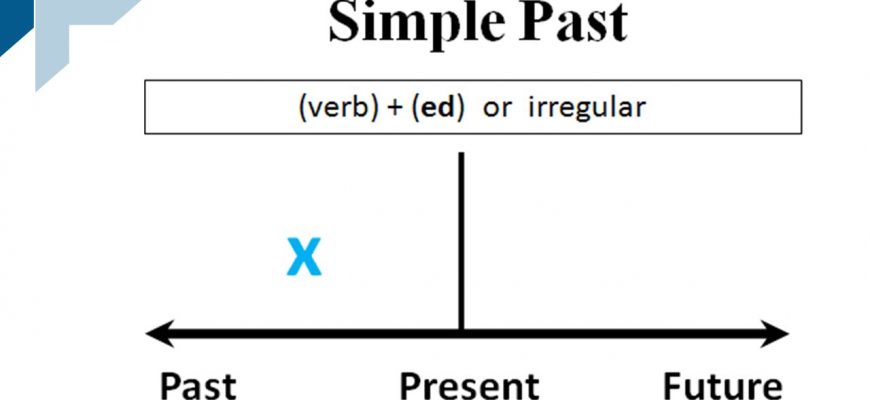
The Simple Past Tense, often just called the Past Tense, is easy to use in English. If you already know how to use the Present Tense, then the Past